Introduction: Despite disease-modifying effects of hydroxyurea (HU) on sickle cell disease (SCD), poor adherence among affected youth commonly impedes treatment impact. The HABIT multi-site randomized controlled efficacy trial aimed to increase HU adherence.
Methods: Youth with SCD ages 10-18 years with impaired adherence were identified through laboratory evidence, primarily flagging levels of treatment-induced fetal hemoglobin (HbF). Eligible youth were enrolled as dyads with their primary caregivers for one year. We tested a 6-month phase of semi-structured supportive, multi-dimensional dyad intervention led by community health workers (CHW) with 4-5 visits addressing information, social issues/referrals, barriers, habit formation using goal-setting and cues, augmented by daily tailored automated text message reminders, compared to standard care. This phase was followed by a 6-month sustainability phase (months 7-12) of observation and, for the intervention group, 1 CHW booster visit. Primary intervention outcomes were 1) HbF levels compared to enrollment; and 2) proportion of days covered (PDC) for HU versus the pre-trial year. The secondary outcome was sustainability of these changes up to month 12.
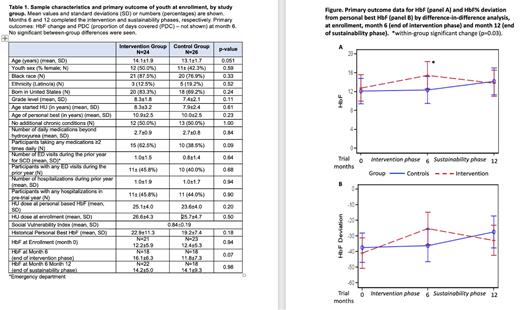
Results: Starting in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted enrollment and clinic-based procedures. The trial enrolled 50 dyads, missing target enrollment. Compared to enrollment levels, both HbF level and PDC significantly improved within the intervention group at month 6 (p=. 03 and . 01, respectfully), with parallel increased MCV (p=.05). Increased HbF did not reach signifance compared to controls (p=.07). No significant within- or between-group differences were found at month 12.
Conclusions: Within-group results suggest that our CHW-based dyad intervention with text message reminders improved HU adherence at 6 months but there were no between-group differences. Effects did not endure through the subsequent 6-month sustainability phase. These findings suggest that improved HU adherence for youth with SCD though our community-based, multi-modal support for youth-caregiver dyads temporarily improved usage. Durability of impact on adherence may require integrating CHW-led support and text reminders into clinical care.
Disclosures
Green:AddMedica: Other: Donated study drug for an NIH-funded clinical trial. Manwani:Novartis, Pfizer, Novo Nordisk, Editas, GBT: Consultancy. Aygun:GBT: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; bluebird bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Smith-Whitley:Pfizer, Inc.: Current Employment.